- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2021 )
- Authors: Kasper Thorup, Lykke Pedersen, Rute R. da Fonseca, Babak Naimi, David Nogués-Bravo, Mario Krapp, Andrea Manica, Mikkel Willemoes, Sissel Sjöberg, Shaohong Feng, Guangji Chen, Alba Rey-Iglesia, Paula F. Campos, Robert Beyer, Miguel B. Araújo, Anders J. Hansen, Guojie Zhang, Anders P. Tøttrup, and Carsten Rahbek
- Link to article: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2023836118
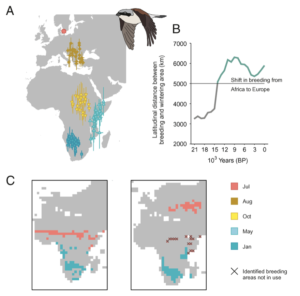
Migration allows animals to exploit spatially separated and seasonally available resources at a continental to global scale. However, responding to global climatic changes might prove challenging, especially for long-distance intercontinental migrants. During glacial periods, when conditions became too harsh for breeding in the north, avian migrants have been hypothesized to retract their distribution to reside within small refugial areas. Here, we present data showing that an Afro-Palearctic migrant continued seasonal migration, largely within Africa, during previous glacial–interglacial cycles with no obvious impact on population size. Using individual migratory track data to hindcast monthly bioclimatic habitat availability maps through the last 120,000 y, we show altered seasonal use of suitable areas through time. Independently derived effective population sizes indicate a growing population through the last 40,000 y. We conclude that the migratory lifestyle enabled adaptation to shifting climate conditions. This indicates that populations of resource-tracking, long-distance migratory species could expand successfully during warming periods in the past, which could also be the case under future climate scenarios.